Pleural Diseases
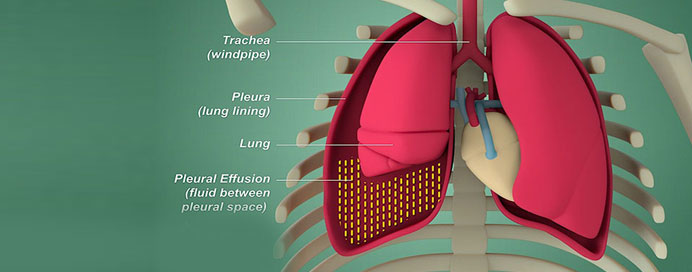
Pleural diseases are conditions that affect the pleura, which is the thin, double-layered membrane that surrounds the lungs and lines the inside of the chest cavity. The pleura has two layers: the visceral pleura, which covers the lungs, and the parietal pleura, which lines the chest cavity. The space between these two layers is known as the pleural space and is filled with a small amount of pleural fluid, which allows the pleura to glide smoothly during breathing.
There are several pleural diseases and conditions, some of which include:
- 1. Pleurisy (Pleuritis): This is inflammation of the pleura and is often caused by viral infections, pneumonia, or other lung infections. Pleurisy can cause sharp chest pain during breathing.
- 2. Pleurisy: This condition involves an abnormal accumulation of fluid in the pleural space. It can result from various causes, including infections, heart failure, cancer, or pulmonary embolism. Pleural effusion can lead to shortness of breath and chest discomfort.
- 3. Pneumothorax: A pneumothorax occurs when air enters the pleural space, causing the lung to collapse partially or completely. It can be spontaneous (without a known cause) or result from trauma or lung disease. Symptoms include sudden chest pain and difficulty breathing.
- 4. Hemothorax: Hemothorax is a condition where there is an accumulation of blood in the pleural space, usually due to trauma or injury to the chest.
- 5. Pleural Thickening: This condition involves the thickening and scarring of the pleura, often as a result of exposure to asbestos. Pleural thickening can lead to restrictive lung disease and reduced lung function.
- 6. Mesothelioma: Mesothelioma is a rare but aggressive form of cancer that affects the pleura. It is primarily associated with asbestos exposure and has a poor prognosis.
- 7. Empyema: Empyema is a collection of pus within the pleural space, typically caused by a bacterial infection. It can result from untreated pneumonia or lung abscesses.
- 8. Pleurodesis: This is a medical procedure used to intentionally cause inflammation and scarring of the pleura. It is done to prevent the recurrence of pleural effusion or pneumothorax.
The symptoms of pleural diseases can vary depending on the specific condition but often include chest pain, difficulty breathing, cough, and sometimes fever. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of clinical evaluation, imaging studies (such as chest X-rays or CT scans), and sometimes procedures like thoracentesis (removing fluid from the pleural space) or biopsy for further evaluation.
Treatment for pleural diseases depends on the underlying cause and can include medications, drainage of pleural fluid, surgery, and in some cases, management of the underlying condition (e.g., antibiotics for infection or chemotherapy for cancer). Early diagnosis and treatment are essential for managing pleural diseases effectively and improving outcomes.